Featured news
The Biomedical & Animal Research News Digest
A new resource housing all the latest news in human and animal health research from the UK and beyond. Take a look inside the BARN Digest for all the major breakthroughs and updates from UAR members and Concordat Signatories!
BARN DigestConnect with us online
Archive news
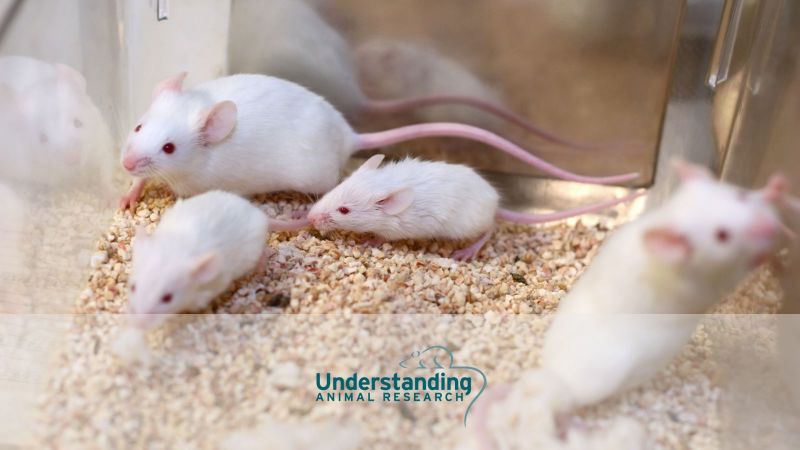
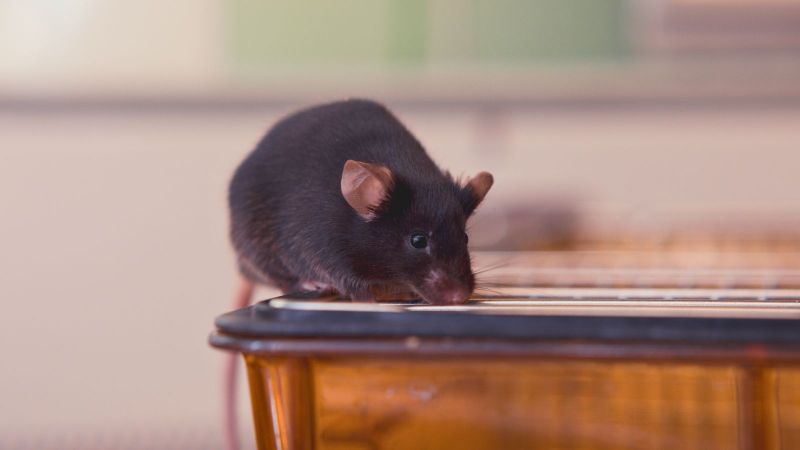
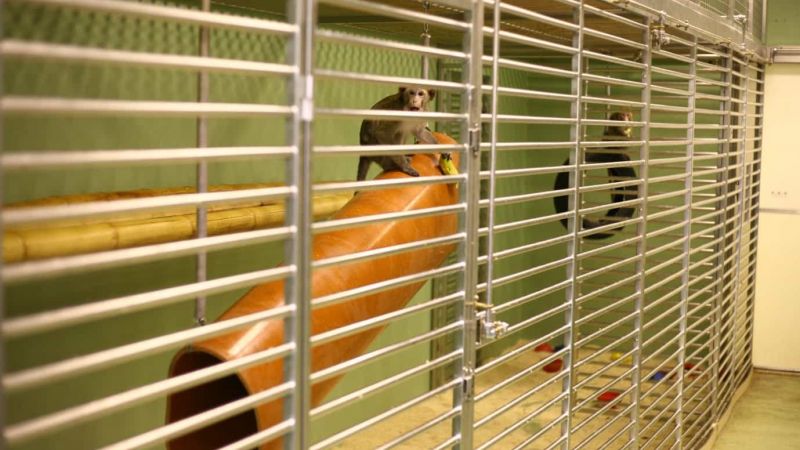
What is animal research?
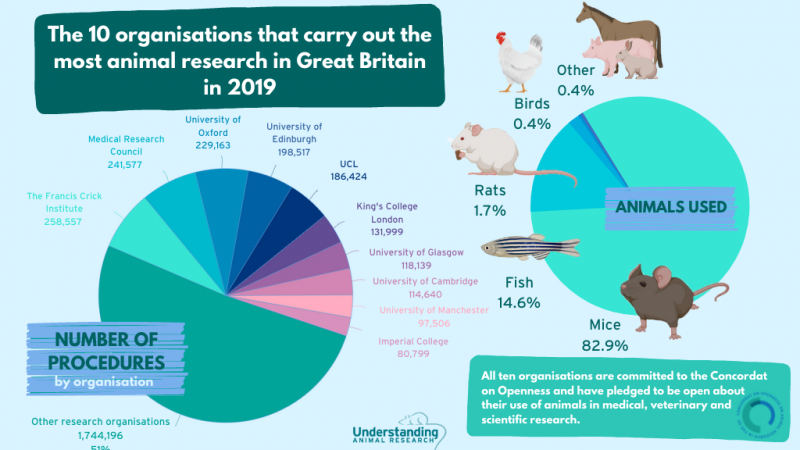
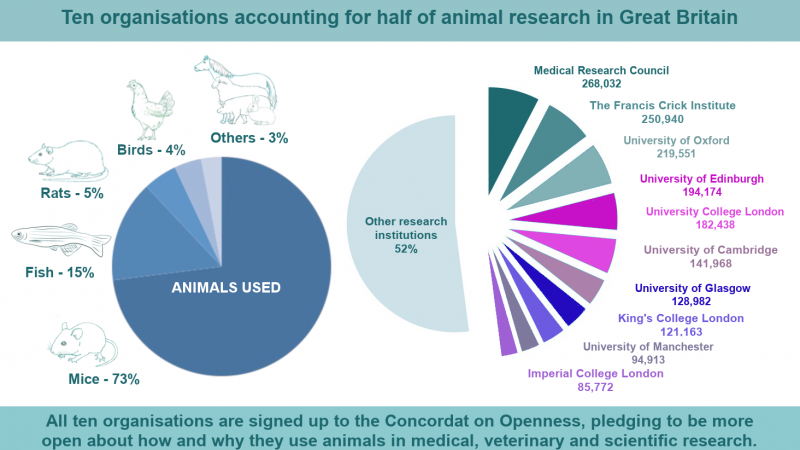
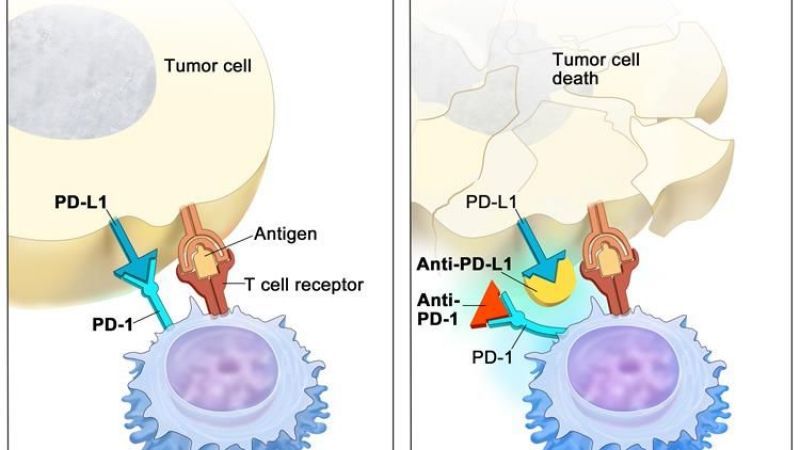
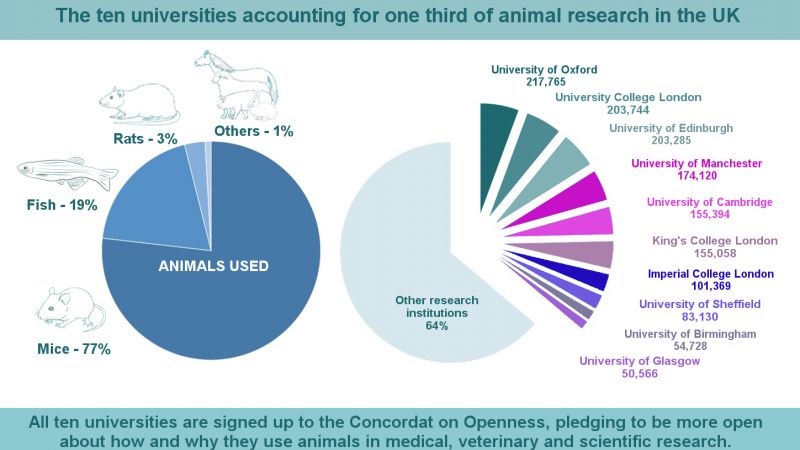
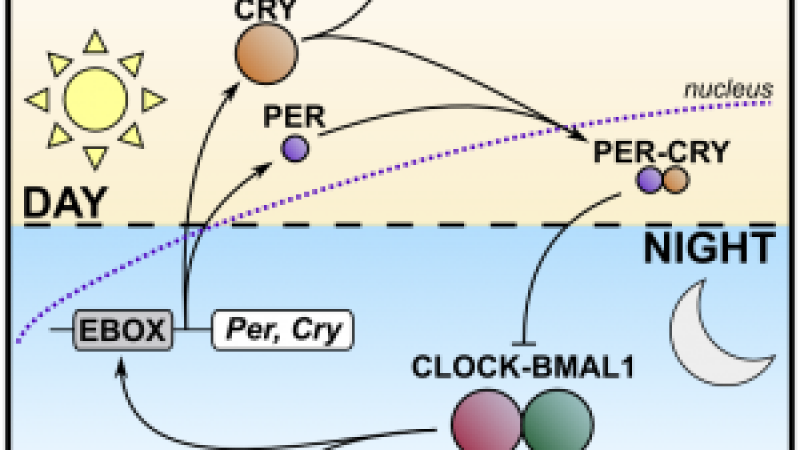
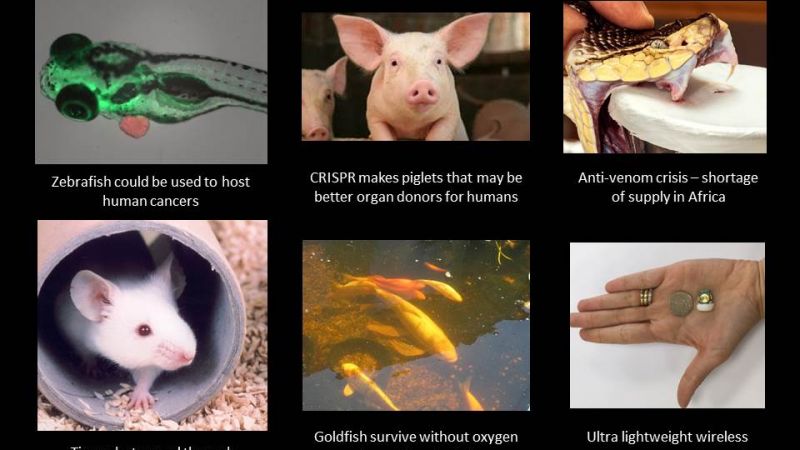
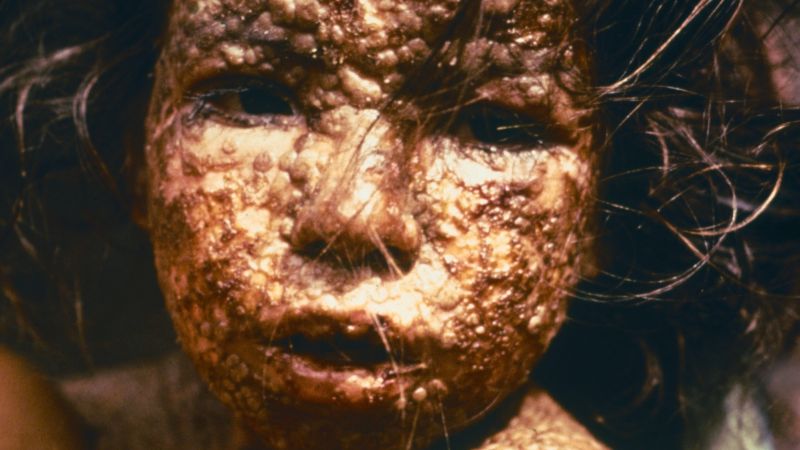
Scientific research using animals is vital to our continued and improved understanding of human and animal health. Animals are used to help us understand living organisms, study disease, and develop and test new medical treatments.
Animal research is also used to keep people, animals and the environment safe from new medicines and chemicals. Animal research is heavily regulated in the UK and can only take place with permission from the Home Office and when there is no other way to do the research.