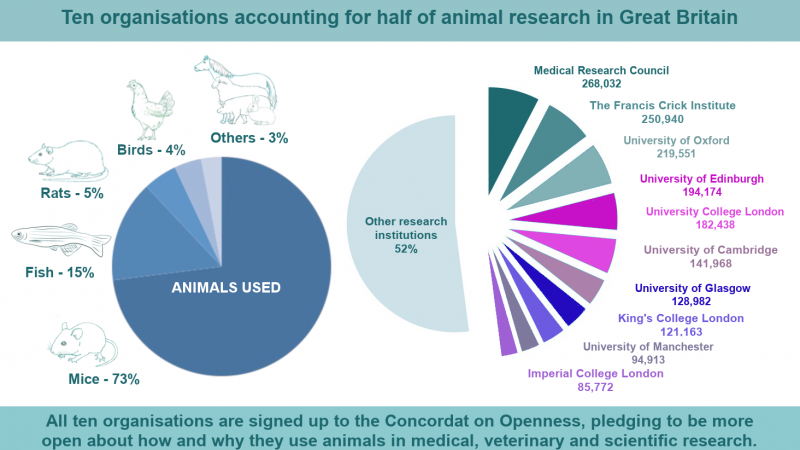
Text to go here...
 Human hearts cannot repair themselves after a heart attack damages heart muscle. However zebrafish hearts can, and the human heart itself is capable of significant growth early in life, so scientists are seeking ways of stimulating human cells to repair the damage to heart muscle caused by heart attacks.
Human hearts cannot repair themselves after a heart attack damages heart muscle. However zebrafish hearts can, and the human heart itself is capable of significant growth early in life, so scientists are seeking ways of stimulating human cells to repair the damage to heart muscle caused by heart attacks.
Scientists have recently found that adult mouse hearts contain stem cells in the epicardium (layer surrounding the heart). Next, scientists stimulated these cells with a small protein called thymosin beta4 before causing limited damage to the heart muscle.
This process gave rise to new heart muscle cells growing to repair the damaged area. The 'repaired' hearts were much stronger than untreated hearts.
Now scientists are seeking more efficient ways to stimulate the stem cells resident in the heart.
Video from the British Heart Foundation
Last edited: 29 July 2022 14:17