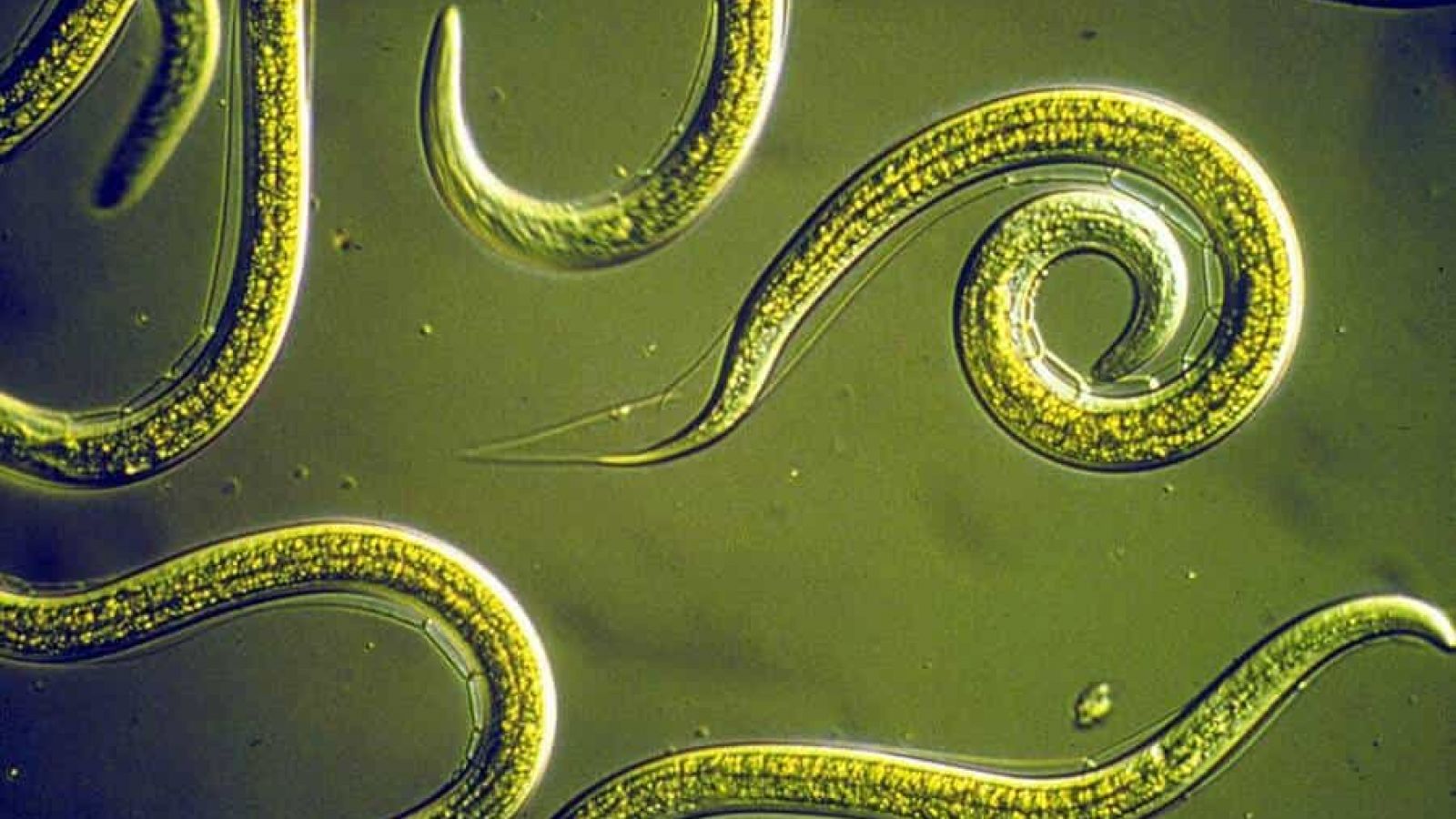
Nematodes, particularly Caenorohabditis elegans, have 'wormed' their way into scientific history, significantly contributing to the research carried out by three winners of the 2002 Nobel Prize for medicine. Despite having a relatively small number of cells, these flatworms still have a nervous system that even includes a primitive brain, making them ideal for studying the development of nerve cells. C elegans was the first animal to have its genome sequenced, back in 1998.
See AnimalResearch.info on C elegans
Recent research in nematodes: Plastics are ruining the sex-lives of worms and could be affecting yours too
View this post on Instagram



