Text to go here...
An innovative new instrument has been developed that enables scientists to observe changes deep inside the brains of animals.
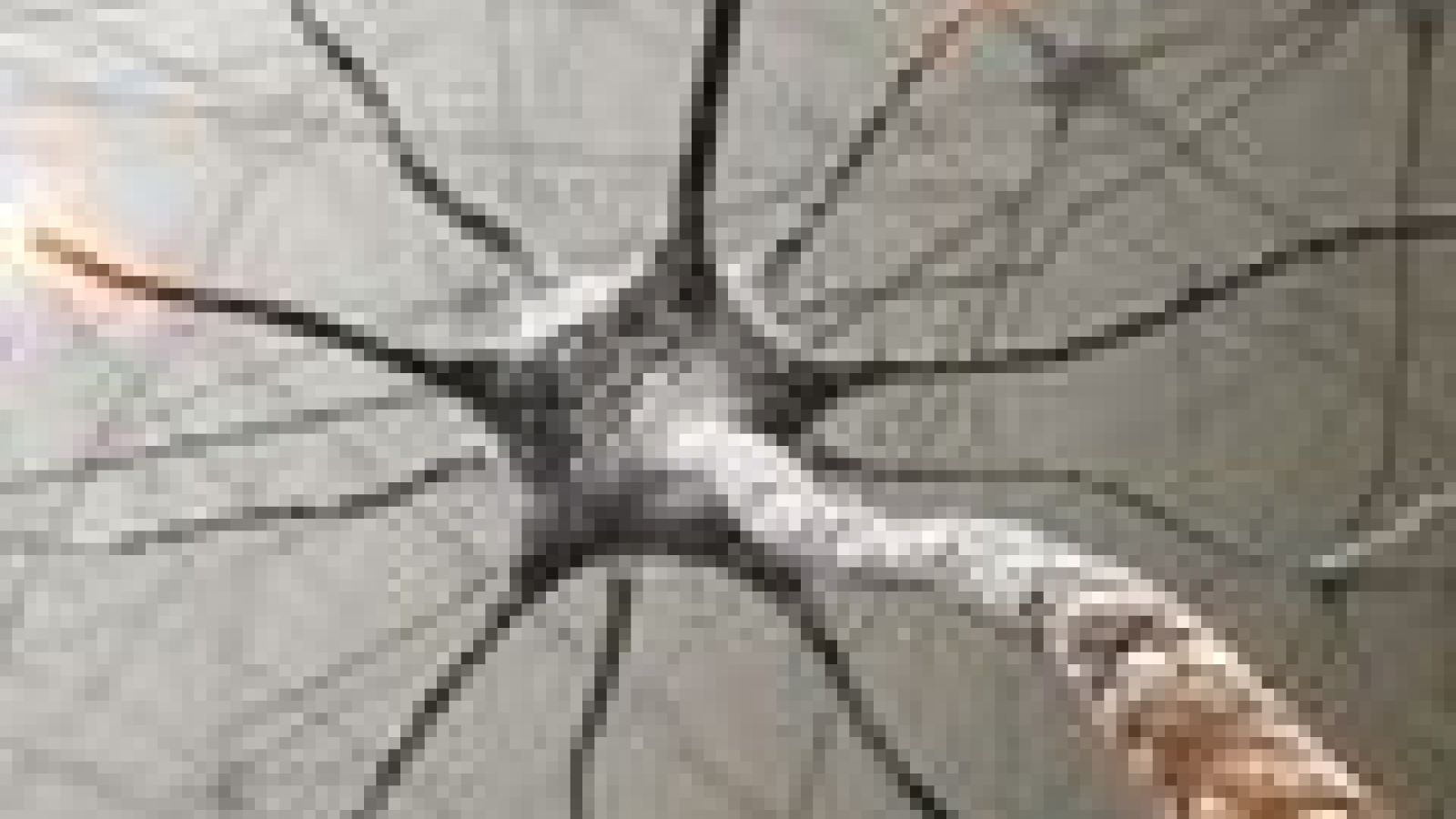
 The micro-endoscope allows scientists to watch nerve cells and blood vessels in animal brains over an extended period of time. Previously, observing inner parts of the brain involved highly invasive surgery and the area of interest could only be looked at once. The new technique enables researchers to look at the same point in the brain many times over days or even weeks.
The micro-endoscope allows scientists to watch nerve cells and blood vessels in animal brains over an extended period of time. Previously, observing inner parts of the brain involved highly invasive surgery and the area of interest could only be looked at once. The new technique enables researchers to look at the same point in the brain many times over days or even weeks.
Observing changes over time will help scientists track the progression of many slowly evolving diseases. For example, the micro-endoscope could watch the damaging changes to nerve connections that are the hallmark of some neurodegenerative diseases. Similarly, the progression of tumour growth and the effectiveness of medicines could be observed with the new instrument.
The tip of the micro-endoscope is 500 to 1000 micrometers in diameter (a micrometer is one millionth of a metre). A glass tube is inserted into the animal's brain to guide the tip to the region of interest. When inserted, the micro-endoscope can take images of the area. After imaging the micro-endoscope is removed and the animal can be returned to its cage. Days or weeks later the instrument can be reinserted to take more pictures of the same area.
The new device has already been used by researchers to explore the structure of neurons in a region of the brain called the hippocampus. The hippocampus is situated deep in the brain and plays an important role in the formation of memories. It was thought the structure of neurons in the region would change with the formation of new memories. But surprisingly the researchers found no change.
The growth of tumour cells in the brains of mice has also been observed with the instrument. Scientists were able to watch how blood vessels in the brain changed as the tumour grew.
This allows scientists to study changes over time without sacrificing animals to see changes at specific time intervals.
Last edited: 11 January 2022 10:49




